Background
An innovative, large footprint mapping and ablation catheter that can toggle between pulsed field ablation (PFA) and radiofrequency (RF) has been introduced, but real-world outcome data are sparse. We report on acute efficacy of linear ablation lesions and initial durability data from remapping procedures.
Methods
All consecutive patients undergoing left atrial (LA) ablation procedures for atrial fibrillation or atrial tachycardias with the lattice-tip catheter were analyzed. Patients provided written informed consent and were enrolled in our prospective TRUST Registry (ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT05521451).
Results
A total of 102 patients (37/102 (36%) women, median age 68 (60–75) years, median left ventricular ejection fraction 60% (53–60)) were enrolled. In 87/102 (85%) patients, linear lesion sets were performed: 34 anterior lines (all blocked, 25/34 (73%) PFA + RF, 9/34 (27%) RF only; median ablation time 6 (4–12) min), 27 mitral isthmus lines (all blocked, 18/27 (67%) PFA + RF, 9/27 (33%) RF only, 5/27 (18%) with additional PFA applied within the coronary sinus; median ablation time 12 (6–25) min), 45 posterior box lesions (all isolated using PFA only; median ablation time 5 (4–8) min), and 23 roof lines (all blocked using PFA only, median ablation time 3 (2–4) min). In 36/102 (35%) patients, a cavo-tricuspid isthmus line was created (all blocked, 30/36 (83%) RF only, 6/36 (17%) PFA + RF; median ablation time 2 (2–4) min). In 7/102 (7%) patients, focal or linear RF applications were applied in the right atrium to treat ongoing atrial tachycardia. Twelve patients (12%) underwent remapping procedures either due to arrhythmia recurrence (8/12; 67%) or during implantation of left atrial appendage (LAA) occlusion devices after previous LAA-isolation (4/12; 33%). All posterior box lesions (7/7) and all mitral isthmus lines (4/4) were durably blocked. In 4/6 cases (67%), reconduction of the anterior line was observed.
Conclusion
The lattice-tip catheter is a versatile tool for linear ablation lesions, achieving high acute efficacy. Initial durability data show promising results regarding the mitral isthmus line and posterior box lesions – both targets with notoriously high reconduction rates after ablation with conventional catheters. More data are needed to further evaluate lesion durability.
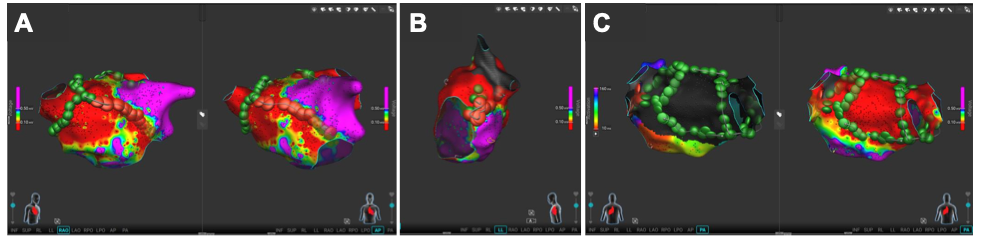
Figure: Linear lesion sets created with the lattice-tip catheter. A) anterior line connecting the mitral isthmus and the anterior aspect of the right superior pulmonary vein. Voltage maps, RAO (left) and a.p. views (right). B) mitral isthmus line, voltage map in left lateral view. C) posterior box lesion in activation (left) and voltage map (right), p.a.-view. Red discs indicate RF lesions, and green discs PFA-lesions.
