Background: The self-expanding (SE) Navitor transcatheter aortic valve, a successor to the Portico valve, has been associated with increased rates of permanent pacemaker implantation (PPI). Optimizing implantation strategies - such as low implantation and commissural alignment - and improving patient selection based on conduction disturbances may mitigate this risk.
Methods: Between June 2021 and April 2025, 350 patients with severe native aortic stenosis underwent TAVI using the SE Navitor (n = 311) or Navitor Vision valve (n = 39). Predictors of PPI were assessed using multivariable logistic regression. Clinical endpoints were adjudicated according to VARC-3 criteria.
Results: Technical success was achieved in 97.4% of cases, and device success in 90.6%. The overall PPI rate was 17.8%. Favorable hemodynamic outcomes were demonstrated by low mean transprosthetic gradients (7.0 mmHg [IQR 5.0–9.0]), a low rate of ≥mild paravalvular leak (1.8%), and a very low incidence of severe prosthesis–patient mismatch (0.3%). Over time, PPI rates declined and were independently associated with atrioventricular block (OR 2.77; 95% CI 1.33–6.26; p=0.007), right bundle branch block (OR 4.32; 95% CI 1.66–11.2; p=0.003), and implantation depth (OR 1.25 per mm; 95% CI 1.09–1.44; p=0.002) in a multivariable model excluding patients with baseline pacemakers, see Figure 1 and 2.
Conclusion: TAVI with the SE Navitor valve demonstrated high technical success and favorable hemodynamic performance. Although the PPI rate was moderate, it was closely linked to pre-existing conduction abnormalities and implantation depth. These findings underscore the importance of careful preprocedural ECG evaluation and precise implantation technique to reduce conduction-related complications in contemporary TAVI practice.
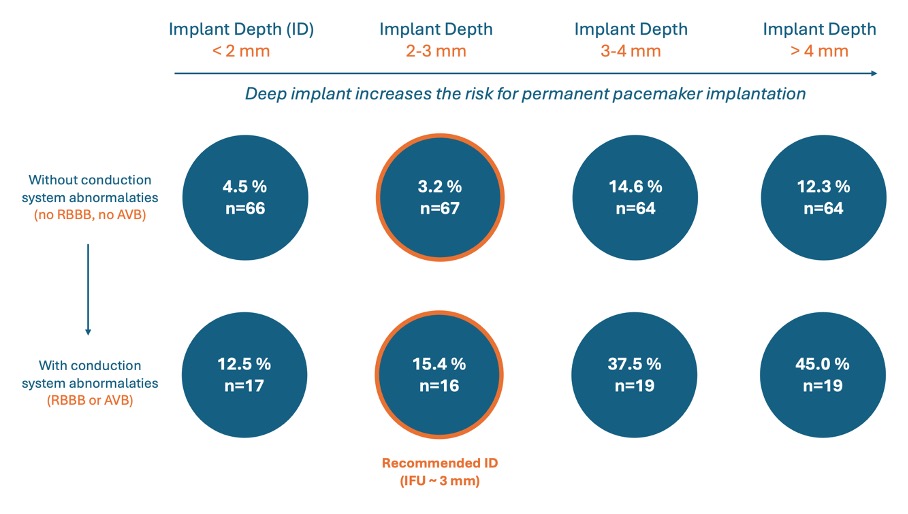
Figure 1: Pacemaker implantation rate by implant depth quartiles and conduction system abnormalities with the self-expanding NAVITOR valve
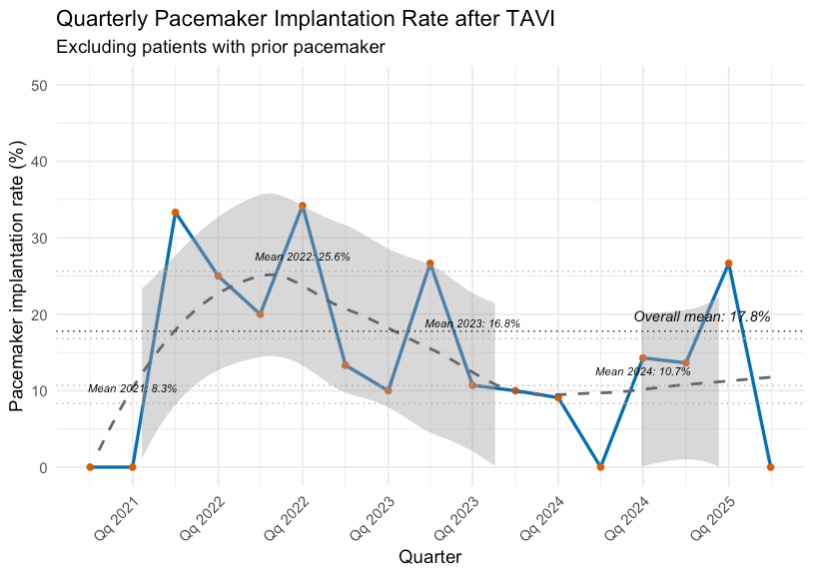
Figure 2: Temporal trend for pacemaker implantation rate with the self-expanding NAVITOR valve
