Background and Aims: Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a potent endogenous vasoconstrictor mainly produced by vascular endothelial cells, and dysregulated ET-1 accumulation is associated with adverse vascular disease development including atherosclerosis. While the Endothelin Receptor A (ETA) mainly facilitates vasoconstriction, the Endothelin Receptor B (ETB) promotes ET-1 clearance and maintains vascular homeostasis. Since some macrophages express ETB, we now aimed to elucidate the involvement of resident vascular macrophages in ET-1 clearance and ETB promoted atherosclerosis
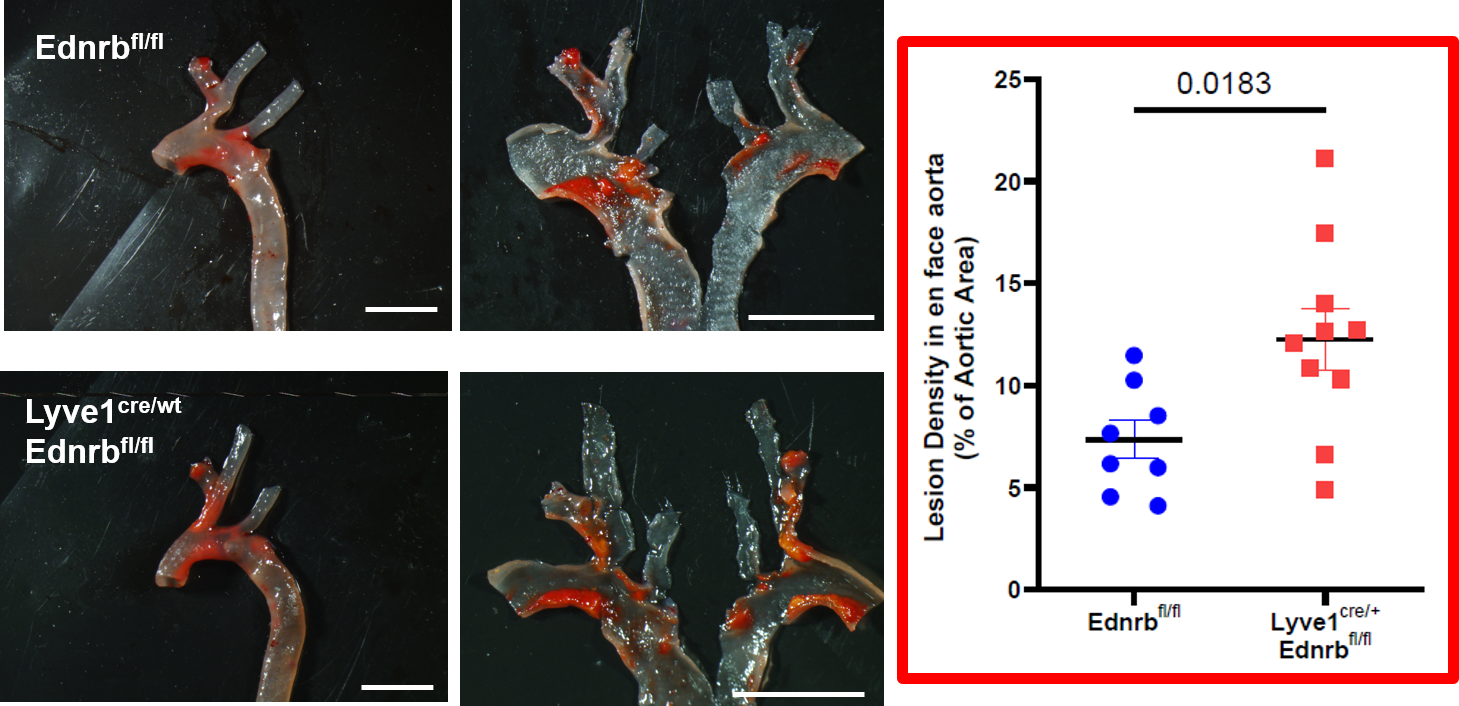
Methods and Results: By exploiting transcriptomic dataset and performing immunofluorescence analysis in human and murine arteries, we detected that adventitial LYVE-1+ macrophages differentially express ETB (EdnrB) gene among macrophage subsets both during homeostasis and atherosclerosis. As assessed by ELISA, we found that sorted LYVE-1+, but not LYVE-1- macrophages mediate ET-1 clearance in vitro. In mice lacking ETB on LYVE-1+ macrophages (Lyve-1cre/wtEdnrBflox/flox) we identified elevated plasma ET-1 level at homeostasis compared to floxed control. Atherosclerotic Lyve-1cre/wtEdnrBflox/flox mice developed through AAV8-induced mPCSK9 overexpression displayed greater aortic ET-1 accumulation as well as exacerbated aortic plaque density and necrotic core within the aortic sinus compared to EdnrBflox/flox control despite comparable plasma cholesterol level (Fig. 1).
Conclusions: Resident adventitial LYVE-1+ macrophages express ETB and promote ET-1 clearance. Deleting ETB in LYVE-1+ macrophages aggravates atherosclerotic lesion development in hypercholesterolemic mice.
Fig. 1: Augmented atherosclerotic lesion density in the aorta of Lyve-1cre/wtEdnrBflox/flox mice compared to flox control 12 weeks after PCSK9 injection and high fat diet. Left, representative photomicrographs of aortic sinus atherosclerotic plaques stained with Oil Red O. Right, quantification of the aortic lesion density (% of aortic area), p=0,0183.